SQL Server's built-in scalar Logical Functions (IIF() and CHOOSE()):
The two new scalar functions introduced under the newly created logical function category are
SQL Server 2012 adds many new built in functions to the exiting sql function cateogories. The new functions that are added to the existing sql function categories are given below,
- String Functions
- FORMAT()
- CONCAT()
- Conversion functions
- PARSE ()
- TRY_PARSE ()
- TRY_CONVERT ()
- Date and time functions
- DATEFROMPARTS ()
- DATETIMEFROMPARTS ()
- DATETIME2FROMPARTS ()
- SMALLDATETIMEFROMPARTS ()
- DATETIMEOFFSETFROMPARTS ()
- TIMEFROMPARTS ()
- EOMONTH ()
Exceptions in SQL SERVER 2012
In C sharp we are having Exceptions(Try, Catch,throw). But in sql server 2008 we are having only Try, Catch. But in SQL SERVER 2012 , a new feature is introduced that is throw.
Syntax:
BEGIN TRY
-----SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
throw
END CATCH
Example:
BEGIN TRY
DECLARE @VALUE INT
SET @VALUE = 1/ 0
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
THROW
END CATCH
New Functions:
IIF() Function:
The IIF function is used to check a condition.
Example : If we have two values with a,b. If the first expression is true, than it returns a value, if the second expression is true, it returns b value.
Example:
DECLARE @X INT;
DECLARE @Y INT;
SET @X=2
SET @Y=3;
SELECT iif(@X>@Y, 'x is greater', 'y is greater') As IIFResult
It is similar to an Array, we can retrieve value using Index
Syntax
CHOOSE ( index, value1, value2.... [, valueN ] )
CHOOSE() Function excepts two parameters,
Index: It represent the index . Here index always starts with1.
Value: List of values of any data type.
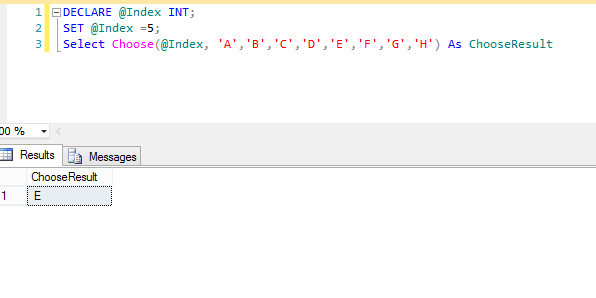
DECLARE @Index INT;
SET @Index =5;
Select Choose(@Index, 'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H') As ChooseResult
Example:
DECLARE @Index INT;
SET @Index =10;
Select Choose(@Index, 'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H') As ChooseResult
If the value has a float data type , then the value is implicitly converted to an integer
DECLARE @Index INT;
SET @Index =1.5;
Select Choose(@Index, 'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H') As ChooseResult
Output:
TRY_PARSE()
If it is successfull, it returns the value, otherwise it returns Null
Syntax
TRY_PARSE ( string_value AS data_type [ USING culture ] )
TRY_CONVERT():()
It returns , Null if fail, Else it returns the Output.
Example:
DATEFROMPARTS Function
Syntax:
DATEFROMPARTS ( year, month, day)
The Eomonth Function:
It returns the last date in the month
MONTH ( startdate [,month_to_add ] )
Example:
If it is successfull, it returns the value, otherwise it returns Null
Syntax
TRY_PARSE ( string_value AS data_type [ USING culture ] )
Example
SELECT TRY_PARSE('Date' AS datetime USING 'en-GB');
SELECT Try_Parse ('Sunday, 13 Feb 2015' AS Datetime2 USING 'en-US') AS [Try_PARSE]
SELECT CASE WHEN TRY_PARSE('DATE' AS DATETIME2 USING 'EN-GB') IS NULL THEN
'PARSE FAIL'
ELSE
'PARSE SUCCESS'
END
TRY_CONVERT():()
TRY_CONVERT function is very similar to the CONVERT function except that it returns NULL when the conversion cannot be completed.It returns , Null if fail, Else it returns the Output.
Example:
SELECT TRY_CONVERT(datetime, '2014/05/31');
SELECT TRY_CONVERT(datetime, '2042-05-31');
SELECT TRY_CONVERT(datetime, '20420434');
SELECT TRY_CONVERT(datetime, '31-12-2012');
DATEFROMPARTS Function
Syntax:
DATEFROMPARTS ( year, month, day)
DECLARE @YEAR AS INT=2015
DECLARE @MONTH AS INT=02
DECLARE @DAY AS INT=13
SELECT DATEFROMPARTS(@YEAR, @MONTH, @DAY)
The Eomonth Function:
It returns the last date in the month
MONTH ( startdate [,month_to_add ] )
Example:
SELECT EOMONTH(GETDATE())ASMONTH









No comments:
Post a Comment